6. Dashboard and Monitoring
6.1. Getting Started with GMT Implementation
When a country starts GMT implementation, it will not deploy the GMT in all regions at once. Rather, this will be a step-wise process. Thus, the first step is to define what areas are going to use the GMT. Once this has been defined, those areas will have to be activated in GMT. This is why the dashboard shows no data for an area as long as its participation has not been activated.
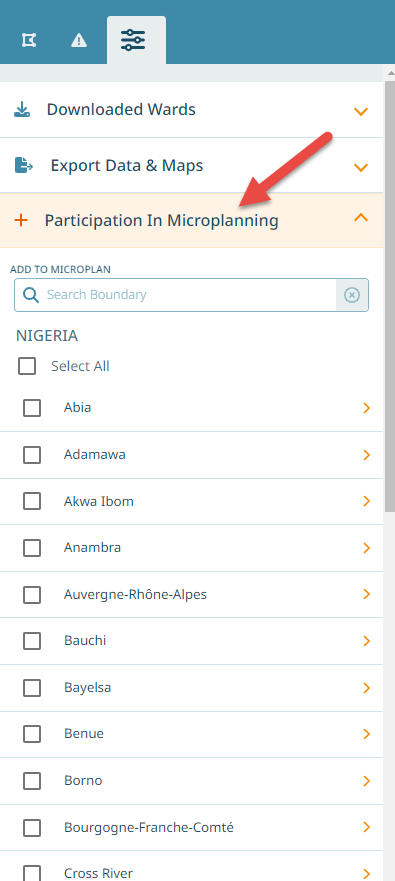
To activate an area, navigate to the ‘Settings’ tab.
In the section ‘Participation in Microplanning’ you can activate the areas that should participate. Note, once participation has been activated, this region will be considered for microplanning in GMT and the data and statistics will be visible.
Note
This section is role based. A defined set of permissions is needed to enable participation for a boundary.
6.2. Dashboard Data and Statistics
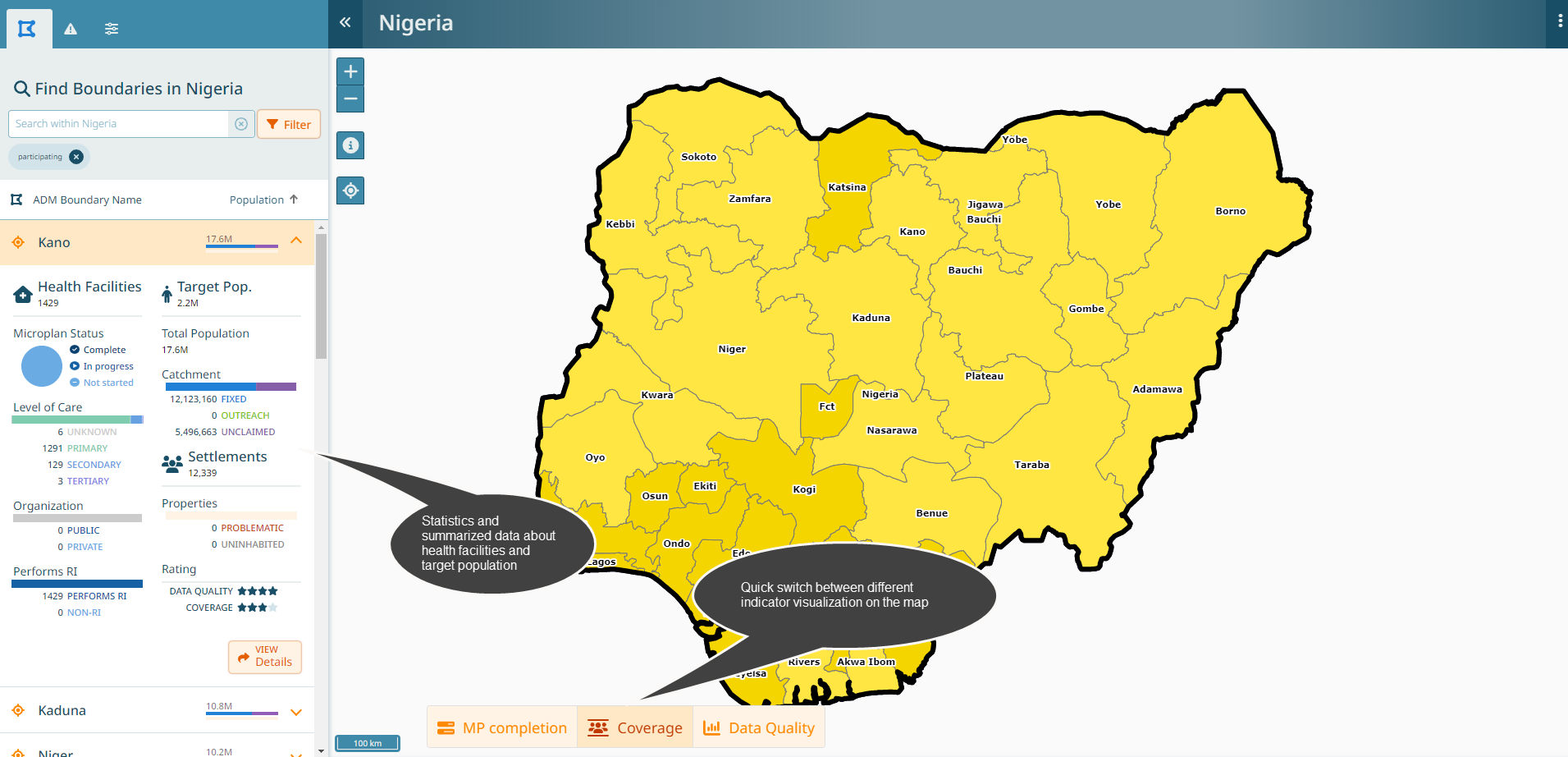
For all boundaries that have been activated, you have an overview of:
Health facility statistics and their microplanning status
Total and target population in that boundary
Settlements that require special attention
Coverage by routine immunization strategy (fixed post, outreach)
Data quality (number of machine generated names)
Note
Target population corresponds to the routine immunization target group, calculated as follows:
0-11 months: 3.8% of total population
12-23 months: 3.5% of total population
Pregnant women: 5% of total population
Important
All dashboard statistics are only updated when data is synchronized. Thus, if the field team is doing microplanning in an area where there is no connectivity, even if they are entering data and updating the microplan, all these changes will only be visible on the dashboard once the synchronization has been performed!
Hint
You can switch between a map that shows microplan completion status, coverage status and data quality status. You can also zoom to different levels to see where the most important areas to focus on are.
6.3. Monitoring Microplanning Progress
The dashboard provides several ways to monitor the progress of microplanning activities:
6.3.1. Completion Status
Track which wards have completed their microplanning activities and which are still in progress. Health facilities are marked with different statuses:
Not Started - Microplanning has not begun
In Progress - Currently being worked on
Complete - Microplanning finished and ready for implementation
6.3.2. Coverage Analysis
Monitor population coverage across different service delivery strategies:
Fixed Post Coverage - Population served by fixed post health facility services
Outreach Coverage - Population served by outreach site services
Unclaimed Population - Population not covered by any service delivery point
6.3.3. Data Quality Assessment
Track the quality of data being collected:
Machine-generated names that need to be updated with proper settlement names
Missing health facility information (ownership, services, etc.)
Boundary issues that need resolution
Population discrepancies that need to be reviewed
6.4. Resetting Microplanning Periods
Once a round of microplanning has finished, the microplanning status on the dashboard needs to be reset for the next planning cycle. This is possible at the State level.
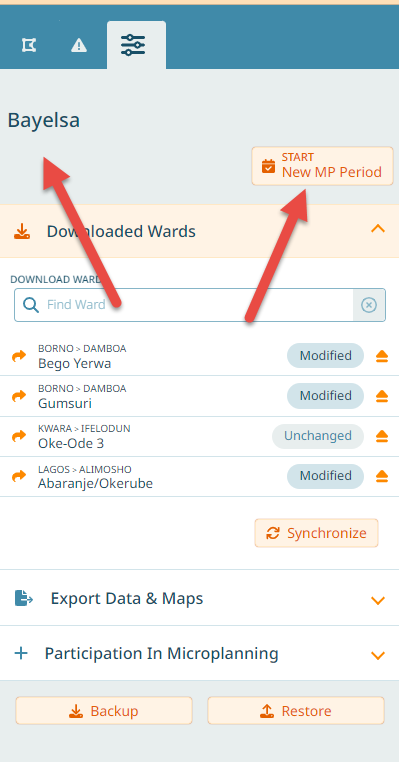
To reset microplanning:
Navigate to the ‘Settings’ tab
Click on ‘Start New MP Period’
Confirm the reset action
Note
This function is role based. A defined set of permissions is needed to reset microplanning for a State.
6.4.1. Impact of Resetting
When microplanning is reset:
All health facility statuses return to “Not Started”
New planning cycle begins
Dashboard statistics reset for fresh monitoring
6.5. Best Practices for Dashboard Monitoring
6.5.1. Regular Monitoring Schedule
Daily checks during active microplanning periods
Weekly progress reviews with district focal persons
Monthly quality assessments of data completeness
6.5.2. Communication Protocols
Regular update calls with sub-district focal persons
Issue escalation procedures for problem areas
Feedback loops to improve data quality
6.5.3. Quality Assurance
Cross-reference dashboard data with field reports
Validate population coverage calculations
Review boundary corrections before approval
Monitor synchronization status to ensure data currency
6.5.4. Performance Analysis
Compare completion rates across similar wards
Identify best practices from high-performing areas
Track improvement over multiple planning cycles
Analyze coverage gaps and resource needs